Save the date

Get ready to Spark, we’re happy to announce Spark the Change 2018 will be happening next June in Paris. We will announce speakers soon. We can’t wait to see you there!

Your Engineering Team Is Not an Island: Success Demands a Holistic View of the Business
I just re-read the awesome post from my friends David Loftesness and Raffi Krikorian, What Does A VP of Engineering Do Again? And while I agree with everything that they say, I think there is one crucial item missing, which has been present in every job I’ve had because all of them were user-facing internet services and a majority of my job has been working with product teams. Collaboration with stakeholders (especially with product) is key, but if you take it one step further, a VP of Engineering is actually measured by execution in a wider context across many teams or departments. You cannot look at engineering in isolation for your successes or failures.
But first a short story about my first months at SoundCloud. The CTO wanted more front-end work done because an important release was nearing. He asked me to hire more engineers to accomplish that goal. I started recruiting, but then I looked at why the velocity of the existing team was not meeting expectations. So, I went to all of the front-end teams (at that time it was Web, iPhone, and Android) and asked a very simple question “What slows you down the most in your day-to-day work?” To my surprise, everyone gave the same answer “We only have one designer.” They went on to say that although the designer was very good, she was completely overloaded so designs, changes, and simple clarifications took forever to get done.
Now that I knew design was actually the cause for delays, the solution to my problem was not to hire more engineers (which might have even made the problem worse with more work for the designer), but to start building a design team.
Engineering leads need to look at the whole product process (together with the responsible stakeholders) and not just at engineering in isolation. What I did was a very simple (but, in this case, effective) form of value stream mapping. Our self-improvement at SoundCloud continued. You can read Phil Calcado’s excellent post about the organizational aspects of microservices at SoundCloud.
The Best Engineering Leads Will Stop and Assess the Situation
Continually assessing situations in a holistic way isn’t just the job of an engineering lead — everybody involved should take responsibility. But, in my experience, the problem usually surfaces in engineering because when things are not moving fast enough (and when do they ever?) management’s first reaction can be to throw more engineers at the problem so more work will get done, but also (and this is the not so nice scenario), management thinks the engineers are not working hard enough. Other common responses from management include reorganizing the teams or adopting new methodologies. However, as an engineering leader, you are a lot like a doctor: you need to diagnose the illness before treating the symptoms.
Engineering leaders need to look at the whole value chain and to sit with the leaders from affected departments to review at the problem. The solution to a problem might not be to hire more people (which a lot of startups do), but to organize product development in a better way. And if you have to hire, it might mean that you have to move headcount around. When everyone has the same goal goal — delivering more business value — shifting headcount from engineering to design or to recruiting shouldn’t be an issue. Afterall, the goal is more business value, not having the biggest department. So, when I realized our problem at SoundCloud wasn’t going to be fixed by adding more engineers, we created a design team. But this was just the first step towards a better setup.
Even after creating a larger design team, it remained isolated from other departments and was not fully integrated with our workflows. The problems of turnaround and wasted resources were exacerbated by the increasing risk of misalignment between product, design, and engineering. Therefore, the next logical step was to improve the organization by creating a delivery team per product.
Shifting Organizational Structures to Deliver Business Value
A delivery team is a team that can deliver the vast majority (95%) of its backlog items to production without dependencies on other teams. Unlike more horizontally-oriented teams (for example, a front-end engineering team that relies on the back-end engineering team for any back-end changes), a delivery team has all the necessary skills inside their team. So, depending on your company and your product, these teams can look very different. In engineering teams that are infrastructure focused, these teams can consist of only engineers; but if you look at a team that delivers a consumer-facing web app, then the team looks more like this:
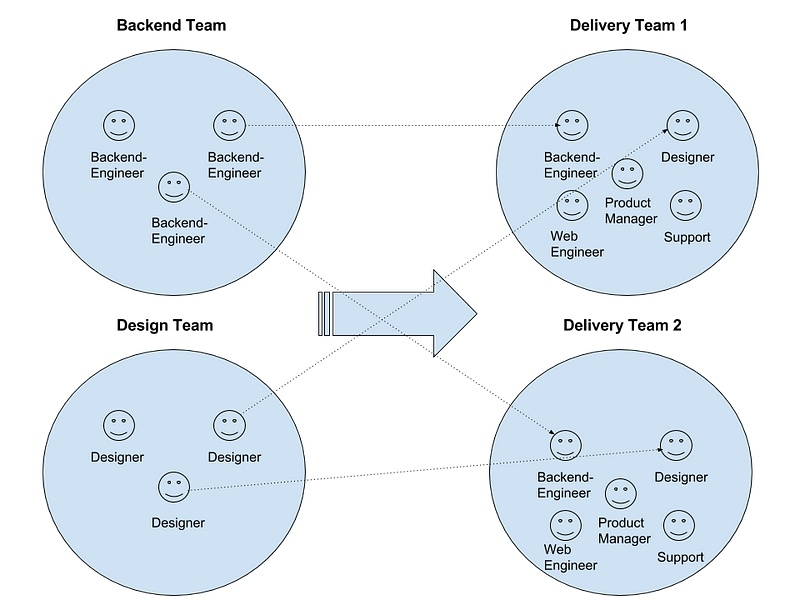
Creating these delivery teams and then making sure you have the right staffing for them should eliminate a staffing mismatch between the affected departments. Some team members (like support) might just be a pointperson for the team, e.g., the support person only attends the daily standup and reports what is going on.
So, don’t look at engineering in isolation when trying to solve delivery problems. It is critical that each engineering leader (and especially the VP of Engineering, who can really influence the organizational setup) ensures that the overall product development process is set up in a way that reduces waste and delivers value to the customer which is the whole point of product development in the first place!
This post includes material from the upcoming book “Scaling Teams” by myself and David Loftesness, which will be published by O’Reilly in 2016. In this book, we will explain in detail the various scaling challenges of software startups.
Thanks to Laurel Ruma and David Loftessness
By: Alexander Grosse from issuu

Free the office slaves
Free the office slaves: No more working day.
The 9-5 working day has come to signify office slavery.
In actual fact though, most knowledge workers work longer than 8 hours a day. A 2011 survey (ASHE) suggests that the average manager in the UK works over 9 hours per day, while extreme hours among certain groups (bankers and lawyers in particular) regularly involved sustained periods of working up to 120 hours a week.
What do set working hours signify?
Extreme hours hurt us. A study by Alexandra Michael, published in 2012, followed investment bankers over a 9 year period. The report concluded that people suffered physical, mental and emotional problems, including depression, a greater number of sick days and relationship breakdown.
Even normal hours often hurt us though. Studies suggest that those in the office spend a large proportion of their time unproductively. They might be checking personal emails or social media sites, or simply carrying out their basic work in a very un-productive fashion. Anyone spent ages staring at a spreadsheet unable to make head or tail of it? Ever fallen asleep in a meeting when supposed to be coming up with ground-breaking new ideas?
The energy cycle
Energy, creativity and brilliance rarely arrive on demand. Instead, human beings work in cycles. We can focus for limited amounts of time. After that we need rest in order to recover.

The ‘ultradian’ pattern, as it is known, normally depends on working in cycles of 90 minutes, with energy troughs in between – normally of about 20-30 minutes. The working day takes no notice of this, however.
Sometimes of course, we enter that wonderful state that Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi referred to as ‘flow’ – where we are hardly aware of the passing of time because we are so absorbed by what we are doing. When we manage to achieve this, the idea of cutting it off with a commute home or a lunch hour seems crazy.
Manage energy, not time
Radical companies understand the need to manage energy, not time. Sometimes that means that workers can work far in excess of the normal working day – developer stories of being so absorbed in a problem they didn’t leave the office until 3am are common. At other times it means workers do far less than the traditional 8 hours and in a different way – starting late, for example, leaving early to pick up children; taking a walk.
No working day means that life and work are more closely blended. It’s not unusual for radical managers to answer emails late at night or to come up with ideas as they sit on a beach with their family. They are not oppressed by this (“oh no! the phone is beeping again!”), partly because they are just as capable of taking a nap when they feel like it or running errands in the middle of what others would call the ‘working day’.
Being Radical
Leo Widrich is a co-founder of Buffer, a company which allows people to manage multiple social media accounts more easily. He manages his own day by splitting it into 90-minute windows and then achieving a certain number of tasks – one per window. A side benefit is that this helps increase focus on just one task at a time, eliminating much of the cost of task-switching. He then tries to plan his rest periods. Instead of allowing these to be filled up with emails or meetings, he goes out for a snack or reads a book. This ensures genuine downtime that allows the brain to recharge and creative ideas to swim up from the subconscious.
So what should we do?
It’s simple really – set people free to work as much as they want, when they want.
There’s no need to say ‘do you mind if I leave early today because blah blah blah’. Just go. It can help to share with others what you’re doing and how to get hold of you so they can co-ordinate with you, but there’s no need to ask permission.
Nor is there any need for that irritating parade of being the last to leave the office, or the first to get there. If someone is emailing late at night it’s because she had a thought and wanted to communicate it, not to demonstrate how dedicated she is.
Some managers might start sweating in light anxiety. How do you know the person won’t bunk off, won’t take advantage, won’t drop their productivity etc.? The answer is that regardless of hours put in people know if someone isn’t pulling their weight or isn’t performing. You can still ask poorly performing people to buck up or get out. But most people want to do well and want the company to do well so they work hard, but you’ve created an environment that helps them work effectively.
You can just trust them.
And just that one piece of advice – trust – frees up a lot of your own time in or out of the working day.
By: Helen Walton from Gamevy



