Save the date

Get ready to Spark, we’re happy to announce Spark the Change 2018 will be happening next June in Paris. We will announce speakers soon. We can’t wait to see you there!

Rejecting roles
Rejecting roles: That’s marketing’s job. You need to talk to IT.
Having roles is considered essential by most organisations. We’ve read dozens of business blogs, HR advice articles and even management training courses that insist clearly defined roles lead to better results, greater productivity and higher motivation. Without clear definition of roles, they warn that tasks get missed, no-one takes responsibility, the office is chaotic and individual motivation drops.
We disagree.
The writers of this advice have grasped the outcomes they want – people taking pride in their work, everyone focusing on delivering value, individuals coordinating and collaborating – but they’ve applied the wrong solution.
They’ve confused roles with responsibilities.
That may not sound like a big deal, but we think it is. Rigid role definition has some major downsides. We believe it hurts companies and individuals, costing them in creativity and happiness.
Most organisations intend their role definitions to be a way of signalling particular specialisations, expertise and responsibilities… but instead, the definitions swiftly harden into barriers, marking out territory which is defended against ‘interference’ from others. Have you ever been told to back off by the marketing manager for commenting on the new advert? Been refused access to the code base by the developers, ‘in case you break something’? Been told to leave presentations to ‘the sales guys’ or forecasts ‘the finance guys’? At the extreme, you may have your opinion rejected with a straight-forward ‘well it’s not your job to worry about x, it’s mine!’.
Individuals may also use their role definition as a way of avoiding unpleasant or boring tasks. This ‘that’s not in my job description’ approach ends up making the company less efficient as well as eroding team motivation. I remember organising a last-minute marketing stunt when I worked at Unilever. I was booking a double-decker bus to turn up and I wanted to check it would actually fit into the office forecourt. The marketing assistant nipped down to Reception to check. An hour later, she returned. The security guard had refused to measure the gateway and if it was beneath the dignity of a security guard, then she reckoned it was beneath the dignity of a marketing assistant as well. So I borrowed the security man’s tape-measure and checked the gateway (you could – quite literally – have fitted a bus through there). Anything wrong with doing my own measuring? Absolutely not. Anything wrong with wasting an hour of time arguing about whose job it was? Plenty.
Roles are comfortable – but bad for us
It’s very human to defend our own work and our own opinion. When we can dress this up with the authority of experience, expertise and organisational separation – all the better. Except it isn’t. Rigid role definition acts as a barrier and can stifle innovation. It can also make things slower and less efficient.
If a customer rings up with a problem, they want a solution, not to be told that only part of their problem can be dealt with by this department, and they must be passed on to billing or whoever to deal with the rest of it.
It’s not great for individuals either. Sticking to just one thing may mean our knowledge gets deeper, but also narrower. We can get bored or worse, so convinced of our own expertise that we can’t take on other points of view.
Being Radical: Sticking to the start up way
In many start ups, a lack of defined roles is the default position. There is not enough money to hire specialists – instead developers must learn to present to investors, marketing managers must be able to create and manage their own customer data, and everyone must have a grip on the financial assumptions as well as a grasp of the their product (this often means some grasp of the technology).
When entrepreneurs look back on the early stage of their companies, they often comment on wistfully on the diversity of work and of how close to the customer it meant they were.
Jeff Bezos, CEO of Amazon, recalled being the ‘mailroom grunt’ in the company’s early days, driving books to shipping and courier companies in his 1987 Blazer. But this doesn’t scale, right? Jeff Bezos is not still doing deliveries. Actually, he is. He spends a week every year in the warehouse. It’s not a PR gimmick, because he refuses to set up interviews when doing it. It’s an opportunity to stay connected to his responsibility – leading Amazon – and not the role of CEO. That includes really understanding conditions for employees – something for which Amazon has received a lot of criticism – and staying close to core services like order fulfilment.
Another trick used at Amazon is to have individual employees who have no role at all. Bezos has ‘shadows’, people who simply follow him around. It means there’s always someone free to chase a wild idea or set up an experiment – and it recognises that a responsibility like ‘envision Amazon’s future’ requires several people, not just a single role.
So what should we do?
1. Responsibilities not roles
Some radical companies go for a very broad responsibility ‘provide value to the company’ and say that how this is fulfilled is up to the individual. Others go for more precise responsibilities: ‘help the customer’ or ‘make sure we comply with financial regulations’.
The point is that how you fulfil these needs can require doing tasks which, in other companies, would be seen as belonging to differing roles.
2. Trust people
A lack of roles makes people more responsible, not less. Tasks rarely get missed because everyone knows they have total responsibility for the work – no tester will come pick up the programmer’s bugs; no finance controller will correct over-optimistic projections.
3. Trust people some more
A lack of roles doesn’t mean that everyone will try to do everything. People naturally gravitate towards what they’re interested in and what they’re good at. If someone is convinced she’s a brilliant illustrator and everyone else insists the stick men cartoons are rubbish, she will soon stop.
4. Value dissent not consensus
No roles doesn’t mean you have to design by committee. Heated arguments are common, and that’s fine. Even if people don’t agree at the end of the debate, the important thing tends to be to air the problem. Opinions can be rejected; a decision can still be made, risks can still be taken…
By: Helen Walton from Gamevy

Spark the Change : inspirer les entreprises françaises grâce à des retours sur expérience concrets
Selon un sondage récent de l’Ifop, 91 % des jeunes cadres français pensent que leur entreprise est en train ou va se transformer. Mais pour 47 % des entreprises, la transformation reste aujourd’hui synonyme de « digitalisation ». Elle ne concerne l’évolution du style de management que dans 21 % d’entre elles et la relation client dans seulement 20 %. Pourtant, ces cadres pensent que la priorité devrait être mise sur l’évolution des modes de rémunération des salariés (37 %), l’évolution des styles de management (33 %) et la formation et le développement de compétences (33 %).
Les jeunes cadres français ont bien compris que loin de se cantonner à la digitalisation des processus, la transformation concerne de nombreux aspects de la vie de l’entreprise, et surtout sa culture et son organisation. « Une entreprise ne peut réussir sa transformation digitale si elle n’a initié une profonde transformation en interne » explique Jean-Christophe Conticello, fondateur et CEO de Wemanity.
« L’apparition d’Internet et des technologies associées a bouleversé en profondeur le monde de l’entreprise. Les modes de consommation ont évolué, le temps s’est accéléré, ce qui a entrainé également une profonde évolution des modes de travail. La nécessité de changer est devenue vitale : on ne compte plus les entreprises qui, en hésitant à changer de recette, n’ont pas réussi à se renouveler et ont disparu : Kodak, Virgin Megastore, Nokia, BlackBerry, Yahoo!, etc. Non seulement, la nouvelle génération a compris cette nécessité de changement, mais elle le suscite avec les nouveaux modes de travail qu’elle privilégie. »
 « Spark the Change » : décrypter et inspirer les bonnes pratiques
« Spark the Change » : décrypter et inspirer les bonnes pratiques 
Pour illustrer et expliquer cette évolution, l’événement « Spark the Change » a été créé à Londres en 2014 par Helen Walton et ses associés de Gamevy, avec le soutien de Wemanity, puis décliné en Australie, aux Pays-Bas, en Inde et au Canada. La première édition française sera organisée à Paris, le 26 juin prochain au Théâtre de la Madeleine.
Centré sur le futur du travail et les moyens de repenser l’entreprise de demain, « Spark the Change » propose aux entreprises françaises un programme de conférences de qualité, basé sur des retours d’expérience.
18 experts se succèderont sur scène pour décrypter les tenants et aboutissants de la transformation des entreprises. Parmi eux : Ludovic Huraux, CEO et fondateur de Shapr ; Dirk Ahlborn, CEO Hyperloop Technology ; Anthony Gooch Galvez, Directeur de la communication et des Affaires publiques à l’OCDE ; Anamita Guha, Product Manager, IBM Watson ; Marianne Syed, Executive Director chez Positive Planet UK. Et bien sûr, Arie Van Bennekum, seul rédacteur européen du Manifeste Agile, aujourd’hui Agile Thought Leader chez Wemanity et Jurgen Appelo, CEO et fondateur d’Agility Scales et expert du management 3.0.
3 thèmes principaux
Animées par des professionnels de toutes nationalités qui souhaitent faire évoluer le monde du travail, les conférences « Spark the Change » sont réparties dans trois sessions principales :

- Créer l’entreprise de demain : les différentes étapes pour insuffler un véritable changement dans l’entreprise, sur la base d’un apprentissage continuel, d’une maîtrise totale des technologies et d’une organisation plus agile et réactive.
Jurgen Appelo, CEO et fondateur d’Agility Scales, expliquera notamment dans quelle mesure il est essentiel pour une entreprise d’aider ses collaborateurs à maîtriser continuellement le changement, par exemple via la ludification et d’autres nouvelles pratiques. - Libérer les talents : développer le potentiel de chaque collaborateur, instaurer le bien-être au travail, booster la collaboration et créer un environnement de travail basé sur la confiance.
Anthony Gooch Galvez, Directeur de la communication et des Affaires publiques à l’OCDE, détaillera ainsi « l’Indicateur du vivre mieux » de l’OCDE qui permet de comprendre ce qui contribue au bien-être des individus et des pays, et d’identifier comment susciter plus de progrès pour tous. - « Sparking disruption » : privilégier l’innovation, voire la disruption ; remettre en cause le statu quo ; et valoriser le progrès social, technologique et culturel.

Dans cette session, Dirk Ahlborn, CEO Hyperloop Technology, dévoilera la genèse de la création d’Hyperloop qui, au-delà des records de vitesse et des nombreuses innovations qui le caractérisent, propose surtout de révolutionner l’expérience des usagers du train.
« Spark the Change a été créé pour inspirer les entreprises, à l’heure où elles sont confrontées à plusieurs évolutions stratégiques : la transformation numérique, l’évolution démographique, la co-innovation voire la “coopétition” sur des marchés mondialisés » explique Sabri Ben Radhia, Responsable de l’événement chez Wemanity. « Si Wemanity était présent lors des premières éditions internationales de Spark the Change en tant que sponsor, nous avons repris la marque et sommes devenus son organisateur principal. Réservé à la fois aux entreprises et aux institutions publiques, l’événement a pour objectif de couvrir l’ensemble des aspects relatifs à la transformation des entreprises, sur la base de très nombreux retours d’expérience. Il vise également à aider les entreprises à développer les compétences nécessaires pour mener à bien leur transformation ».
Le programme de la journée a été construit pour privilégier l’échange d’expériences et le networking. 750 personnes issues de l’ensemble de l’écosystème de l’innovation européen sont attendues le 26 juin prochain au Théâtre de la Madeleine.
Aurons-nous le plaisir de vous compter parmi eux ?
Plus d’information sur l’événement : http://sparkthechange.fr/about-us/
Les experts qui interviendront dans les conférences : http://sparkthechange.fr/speakers/
Inscription : http://sparkthechange.fr/tickets/
Also published on Medium.

Your Engineering Team Is Not an Island: Success Demands a Holistic View of the Business
I just re-read the awesome post from my friends David Loftesness and Raffi Krikorian, What Does A VP of Engineering Do Again? And while I agree with everything that they say, I think there is one crucial item missing, which has been present in every job I’ve had because all of them were user-facing internet services and a majority of my job has been working with product teams. Collaboration with stakeholders (especially with product) is key, but if you take it one step further, a VP of Engineering is actually measured by execution in a wider context across many teams or departments. You cannot look at engineering in isolation for your successes or failures.
But first a short story about my first months at SoundCloud. The CTO wanted more front-end work done because an important release was nearing. He asked me to hire more engineers to accomplish that goal. I started recruiting, but then I looked at why the velocity of the existing team was not meeting expectations. So, I went to all of the front-end teams (at that time it was Web, iPhone, and Android) and asked a very simple question “What slows you down the most in your day-to-day work?” To my surprise, everyone gave the same answer “We only have one designer.” They went on to say that although the designer was very good, she was completely overloaded so designs, changes, and simple clarifications took forever to get done.
Now that I knew design was actually the cause for delays, the solution to my problem was not to hire more engineers (which might have even made the problem worse with more work for the designer), but to start building a design team.
Engineering leads need to look at the whole product process (together with the responsible stakeholders) and not just at engineering in isolation. What I did was a very simple (but, in this case, effective) form of value stream mapping. Our self-improvement at SoundCloud continued. You can read Phil Calcado’s excellent post about the organizational aspects of microservices at SoundCloud.
The Best Engineering Leads Will Stop and Assess the Situation
Continually assessing situations in a holistic way isn’t just the job of an engineering lead — everybody involved should take responsibility. But, in my experience, the problem usually surfaces in engineering because when things are not moving fast enough (and when do they ever?) management’s first reaction can be to throw more engineers at the problem so more work will get done, but also (and this is the not so nice scenario), management thinks the engineers are not working hard enough. Other common responses from management include reorganizing the teams or adopting new methodologies. However, as an engineering leader, you are a lot like a doctor: you need to diagnose the illness before treating the symptoms.
Engineering leaders need to look at the whole value chain and to sit with the leaders from affected departments to review at the problem. The solution to a problem might not be to hire more people (which a lot of startups do), but to organize product development in a better way. And if you have to hire, it might mean that you have to move headcount around. When everyone has the same goal goal — delivering more business value — shifting headcount from engineering to design or to recruiting shouldn’t be an issue. Afterall, the goal is more business value, not having the biggest department. So, when I realized our problem at SoundCloud wasn’t going to be fixed by adding more engineers, we created a design team. But this was just the first step towards a better setup.
Even after creating a larger design team, it remained isolated from other departments and was not fully integrated with our workflows. The problems of turnaround and wasted resources were exacerbated by the increasing risk of misalignment between product, design, and engineering. Therefore, the next logical step was to improve the organization by creating a delivery team per product.
Shifting Organizational Structures to Deliver Business Value
A delivery team is a team that can deliver the vast majority (95%) of its backlog items to production without dependencies on other teams. Unlike more horizontally-oriented teams (for example, a front-end engineering team that relies on the back-end engineering team for any back-end changes), a delivery team has all the necessary skills inside their team. So, depending on your company and your product, these teams can look very different. In engineering teams that are infrastructure focused, these teams can consist of only engineers; but if you look at a team that delivers a consumer-facing web app, then the team looks more like this:
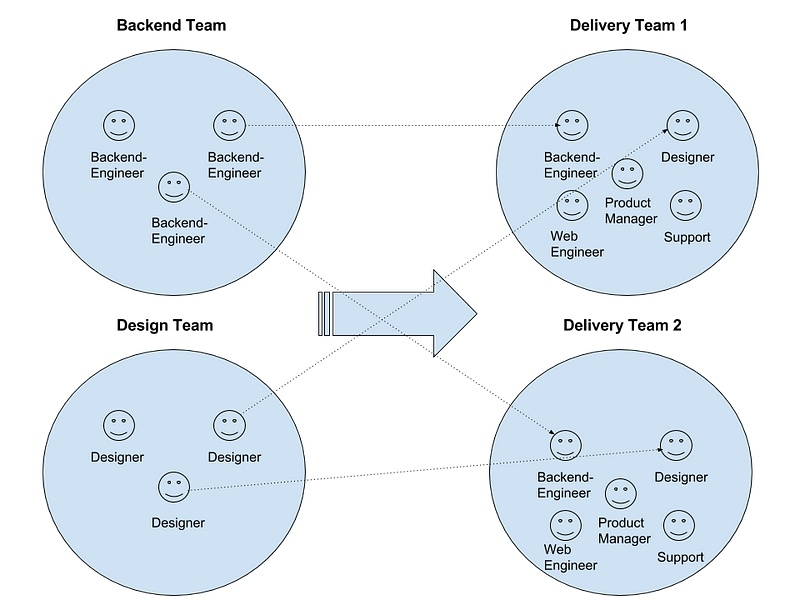
Creating these delivery teams and then making sure you have the right staffing for them should eliminate a staffing mismatch between the affected departments. Some team members (like support) might just be a pointperson for the team, e.g., the support person only attends the daily standup and reports what is going on.
So, don’t look at engineering in isolation when trying to solve delivery problems. It is critical that each engineering leader (and especially the VP of Engineering, who can really influence the organizational setup) ensures that the overall product development process is set up in a way that reduces waste and delivers value to the customer which is the whole point of product development in the first place!
This post includes material from the upcoming book “Scaling Teams” by myself and David Loftesness, which will be published by O’Reilly in 2016. In this book, we will explain in detail the various scaling challenges of software startups.
Thanks to Laurel Ruma and David Loftessness
By: Alexander Grosse from issuu

